2008-07-17 DB Study
Problem
Some time ago, I loaded a large set of data into one my tables. To speed up the load, I disabled the FOREIGN KEY and CHECK constraints on the table and then re-enabled them after the load was complete. I am now finding that some of the loaded data was referentially invalid. What happened?
Solution
Disabling constraint checking for FOREIGN KEYS and CHECK constraints is accomplished using the ALTER TABLE statement and specifying a NOCHECK on the constraint. However, when re-enabling constraints, I've seen many instances where the DBA would re-enable the constraints by specifying CHECK but forget (or not know) to ask the SQL Server engine to re-verify the relationships by additionally specifying WITH CHECK. By specifying CHECK but not additionally specifying WITH CHECK, the SQL Server engine will enable the constraint but not verify that referential integrity is intact. Furthermore, when a FOREIGN KEY or CHECK constraint is disabled, SQL Server will internally flag the constraint as not being "trustworthy". This can cause the optimizer to not consider the constraint relationship when trying to generate the most optimal query plans.
In a Management Studio connection, run the following script to create a parent table called EMPLOYEE and a child table called TIMECARD. TIMECARD rows may only exist provided that the EMPLOYEE row exists
SET NOCOUNT ON
GO
CREATE TABLE DBO.EMPLOYEE
(
EMPLOYEEID INT IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
FIRSTNAME VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
LASTNAME VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL
)
GO
CREATE TABLE DBO.TIMECARD
(
TIMECARDID INT IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
EMPLOYEEID INT NOT NULL,
HOURSWORKED TINYINT NOT NULL,
DATEWORKED DATETIME NOT NULL
)
GO
-- Only allow valid employees to have a timecard
ALTER TABLE DBO.TIMECARD
ADD CONSTRAINT FK_TIMECARD_EMPLOYEEID FOREIGN KEY (EMPLOYEEID)
REFERENCES DBO.EMPLOYEE(EMPLOYEEID)
ON DELETE CASCADE
GO
INSERT INTO DBO.EMPLOYEE (FIRSTNAME, LASTNAME)
SELECT 'JOHN', 'DOE'
GO
INSERT INTO DBO.TIMECARD (EMPLOYEEID, HOURSWORKED, DATEWORKED)
SELECT 1, 8, '2008-01-01'
GO
|
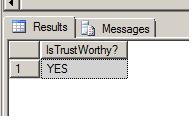
Now run the following query (valid for both SQL Server 2000 and 2005) to check the foreign key constraint's trustworthiness
SELECT CASE WHEN OBJECTPROPERTY(OBJECT_ID('FK_TIMECARD_EMPLOYEEID'), 'CnstIsNotTrusted') = 1 THEN 'NO' ELSE 'YES' END AS 'IsTrustWorthy?'
GO
|
You will see that the SQL Server engine considers the foreign key constraint as referentially valid
Now we'll load some additional data but we'll disable the constraint prior to load. Once the rows are loaded, we'll re-enable the constraint. Typically, a DBA would do this when loading large amounts of data in order to speed up the load. For illustrative purposes, we'll just load 3 new rows.
ALTER TABLE DBO.TIMECARD NOCHECK CONSTRAINT FK_TIMECARD_EMPLOYEEID
GO
INSERT INTO DBO.TIMECARD (EMPLOYEEID, HOURSWORKED, DATEWORKED)
SELECT 1, 8, '2008-01-02'
GO
INSERT INTO DBO.TIMECARD (EMPLOYEEID, HOURSWORKED, DATEWORKED)
SELECT 1, 8, '2008-01-03'
GO
INSERT INTO DBO.TIMECARD (EMPLOYEEID, HOURSWORKED, DATEWORKED)
SELECT 2, 8, '2008-01-04'
GO
ALTER TABLE DBO.TIMECARD CHECK CONSTRAINT FK_TIMECARD_EMPLOYEEID
GO
|
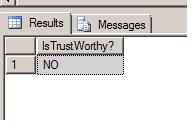
If we now re-examine the constraint's trustworthiness and you will see that the SQL Server engine now does not believe the constraint is trustworthy enough to use in execution plan generation.
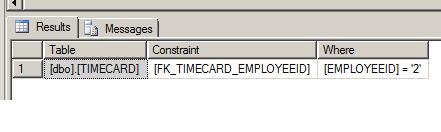
Wait a minute! If you didn't notice, I have an error in my script! The 3rd row I added is for EMPLOYEEID = 2. However, this EMPLOYEEID does not exist in my table! This is because the CHECK issued when the constraint was re-enabled strictly controls re-enabling the constraint; it does not verify that referential integrity is intact. Running DBCC CHECKCONSTRAINTS(TIMECARD) verifies that referential integrity has been violated:
I knew that there was an error in my script. But what if I didn't? This integrity violation would lurk in my database until TIMECARD totals were generated for month-end payroll and the employee's paycheck would be shortchanged by 8 working hours. I can just imagine his displeasure with the Payroll Department for this mistake and Payroll's displeasure with me for letting this squeak through.
This is why it's imperative that you re-enable your constraints by additionally specifying the little known WITH CHECK option. Without specifying WITH CHECK, the SQL Server engine will enable your constraints without checking referential integrity (and as we see, will consider the constraints untrustworthy for query optimization). In the example, if we re-enabled the constraint using the following statement, we would've seen up front that there was an integrity issue with the loaded data.
ALTER TABLE DBO.TIMECARD WITH CHECK CHECK CONSTRAINT FK_TIMECARD_EMPLOYEEID
GO
|
If we fix the erroneous row and then re-enable the constraint correctly, we see that that no referential integrity violation is detected and the constraint can now be trusted by the SQL Server optimizer.
UPDATE DBO.TIMECARD SET EMPLOYEEID = 1 WHERE EMPLOYEEID = 2
GO
ALTER TABLE DBO.TIMECARD WITH CHECK CHECK CONSTRAINT FK_TIMECARD_EMPLOYEEID
GO
SELECT CASE WHEN OBJECTPROPERTY(OBJECT_ID('FK_TIMECARD_EMPLOYEEID'), 'CnstIsNotTrusted') = 1 THEN 'NO' ELSE 'YES' END AS
'IsTrustWorthy?'
GO
|
If you're worried about having untrusted constraints in your database, you can check using the following query (this can be run on both SQL Server 2000 and 2005 databases)
select table_name, constraint_name
from information_schema.table_constraints
where (constraint_type = 'FOREIGN KEY' or constraint_type = 'CHECK')
and objectproperty(object_id(constraint_name), 'CnstIsNotTrusted') = 1
go
|
Next Steps
Related Tips
Forum Posts
주디 테스트 스크립트
SET NOCOUNT ON
GO
-- sample table 생성
IF EXISTS( SELECT *
FROM sysobjects
WHERE name ='TIMECARD')
DROP TABLE DBO.TIMECARD
GO
IF EXISTS( SELECT *
FROM sysobjects
WHERE name ='EMPLOYEE')
DROP TABLE DBO.EMPLOYEE
GO
CREATE TABLE DBO.EMPLOYEE
(
EMPLOYEEID INT IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
FIRSTNAME VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
LASTNAME VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL
)
GO
CREATE TABLE DBO.TIMECARD
(
TIMECARDID INT IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
EMPLOYEEID INT NOT NULL,
HOURSWORKED TINYINT NOT NULL,
DATEWORKED DATETIME NOT NULL
)
GO
-- Only allow valid employees to have a timecard
ALTER TABLE DBO.TIMECARD
ADD CONSTRAINT FK_TIMECARD_EMPLOYEEID FOREIGN KEY (EMPLOYEEID)
REFERENCES DBO.EMPLOYEE(EMPLOYEEID)
ON DELETE CASCADE
GO
sp_helpconstraint TIMECARD
go
--Object Name
--TIMECARD
--
--
--constraint_type constraint_name delete_action update_action status_enabled status_for_replication constraint_keys
--FOREIGN KEY FK_TIMECARD_EMPLOYEEID Cascade No Action Enabled Is_For_Replication EMPLOYEEID
-- REFERENCES judy_test.dbo.EMPLOYEE (EMPLOYEEID)
--PRIMARY KEY (clustered) PK__TIMECARD__403A8C7D (n/a) (n/a) (n/a) (n/a) TIMECARDID
-- sample data
INSERT INTO DBO.EMPLOYEE (FIRSTNAME, LASTNAME)
SELECT 'JOHN', 'DOE'
GO
INSERT INTO DBO.TIMECARD (EMPLOYEEID, HOURSWORKED, DATEWORKED)
SELECT 1, 8, '2008-01-01'
GO
-- 인증된 관계
SELECT
CASE
WHEN OBJECTPROPERTY(OBJECT_ID('FK_TIMECARD_EMPLOYEEID'), 'CnstIsNotTrusted') = 1 THEN 'NO'
ELSE 'YES' END AS 'IsTrustWorthy?'
GO
--Result
--IsTrustWorthy?
--YES
SELECT *
FROM EMPLOYEE
--EMPLOYEEID FIRSTNAME LASTNAME
--1 JOHN DOE
SELECT *
FROM TIMECARD
--TIMECARDID EMPLOYEEID HOURSWORKED DATEWORKED
--1 1 8 2008-01-01 00:00:00.000
-- check option disable
ALTER TABLE DBO.TIMECARD NOCHECK CONSTRAINT FK_TIMECARD_EMPLOYEEID
GO
-- 위배되는 데이타 입력
-- 어랏 입력된다.
INSERT INTO DBO.TIMECARD (EMPLOYEEID, HOURSWORKED, DATEWORKED)
SELECT 1, 8, '2008-01-02'
GO
INSERT INTO DBO.TIMECARD (EMPLOYEEID, HOURSWORKED, DATEWORKED)
SELECT 1, 8, '2008-01-03'
GO
INSERT INTO DBO.TIMECARD (EMPLOYEEID, HOURSWORKED, DATEWORKED)
SELECT 2, 8, '2008-01-04'
GO
INSERT INTO DBO.TIMECARD (EMPLOYEEID, HOURSWORKED, DATEWORKED)
SELECT 3, 8, '2008-01-04'
GO
SELECT *
FROM TIMECARD
GO
--TIMECARDID EMPLOYEEID HOURSWORKED DATEWORKED
--1 1 8 2008-01-01 00:00:00.000
--2 1 8 2008-01-02 00:00:00.000
--3 1 8 2008-01-03 00:00:00.000
--4 2 8 2008-01-04 00:00:00.000
--5 3 8 2008-01-04 00:00:00.000
-- re-check constraint enable setup
-- check 활성화만 시킨다. 앞으로 들어올 데이타에 대한 체크만 이루어짐
ALTER TABLE DBO.TIMECARD CHECK CONSTRAINT FK_TIMECARD_EMPLOYEEID
GO
sp_helpconstraint TIMECARD
go
--constraint_type constraint_name delete_action update_action status_enabled status_for_replication constraint_keys
--FOREIGN KEY FK_TIMECARD_EMPLOYEEID Cascade No Action Enabled Is_For_Replication EMPLOYEEID
-- REFERENCES judy_test.dbo.EMPLOYEE (EMPLOYEEID)
--PRIMARY KEY (clustered) PK__TIMECARD__44FF419A (n/a) (n/a) (n/a) (n/a) TIMECARDID
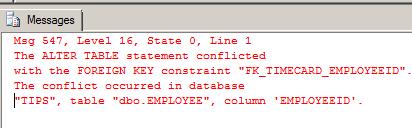
INSERT INTO DBO.TIMECARD (EMPLOYEEID, HOURSWORKED, DATEWORKED)
SELECT 3, 8, '2008-01-04'
GO
--
--메시지 547, 수준 16, 상태 0, 줄 1
--INSERT 문이 FOREIGN KEY 제약 조건 "FK_TIMECARD_EMPLOYEEID"과(와) 충돌했습니다. 데이터베이스 "judy_test", 테이블 "dbo.EMPLOYEE", column 'EMPLOYEEID'에서 충돌이 발생했습니다.
--문이 종료되었습니다.
--현재 fk 관계 체크
SELECT
CASE
WHEN OBJECTPROPERTY(OBJECT_ID('FK_TIMECARD_EMPLOYEEID'), 'CnstIsNotTrusted') = 1 THEN 'NO'
ELSE 'YES' END AS 'IsTrustWorthy?'
GO
--신뢰할 수 없다.
--IsTrustWorthy?
--NO
-- 그렇다면, 어떤 오류가 생긴 거냐
DBCC CHECKCONSTRAINTS(TIMECARD)
GO
--Table Constraint Where
--[dbo].[TIMECARD] [FK_TIMECARD_EMPLOYEEID] [EMPLOYEEID] = '2'
--[dbo].[TIMECARD] [FK_TIMECARD_EMPLOYEEID] [EMPLOYEEID] = '3'
-- 위의 활성화 체크조건 변경
UPDATE DBO.TIMECARD SET EMPLOYEEID = 1 WHERE EMPLOYEEID IN(2, 3)
GO
-- 기존 데이터 체크하면서 제크 조건 추가
ALTER TABLE DBO.TIMECARD WITH CHECK CHECK CONSTRAINT FK_TIMECARD_EMPLOYEEID
GO
sp_helpconstraint TIMECARD
go
--Object Name
--TIMECARD
--
--
--constraint_type constraint_name delete_action update_action status_enabled status_for_replication constraint_keys
--FOREIGN KEY FK_TIMECARD_EMPLOYEEID Cascade No Action Enabled Is_For_Replication EMPLOYEEID
-- REFERENCES judy_test.dbo.EMPLOYEE (EMPLOYEEID)
--PRIMARY KEY (clustered) PK__TIMECARD__44FF419A (n/a) (n/a) (n/a) (n/a) TIMECARDID
SELECT CASE WHEN OBJECTPROPERTY(OBJECT_ID('FK_TIMECARD_EMPLOYEEID'), 'CnstIsNotTrusted') = 1 THEN 'NO' ELSE 'YES' END AS
'IsTrustWorthy?'
GO
--IsTrustWorthy?
--YES
-- 데이타베이스내 제약 오류 정보 추출
select table_name, constraint_name
from information_schema.table_constraints
where (constraint_type = 'FOREIGN KEY' or constraint_type = 'CHECK')
and objectproperty(object_id(constraint_name), 'CnstIsNotTrusted') = 1
go
 invalid-file
invalid-file